Understanding How Water Ionizers Transform Your Tap Water
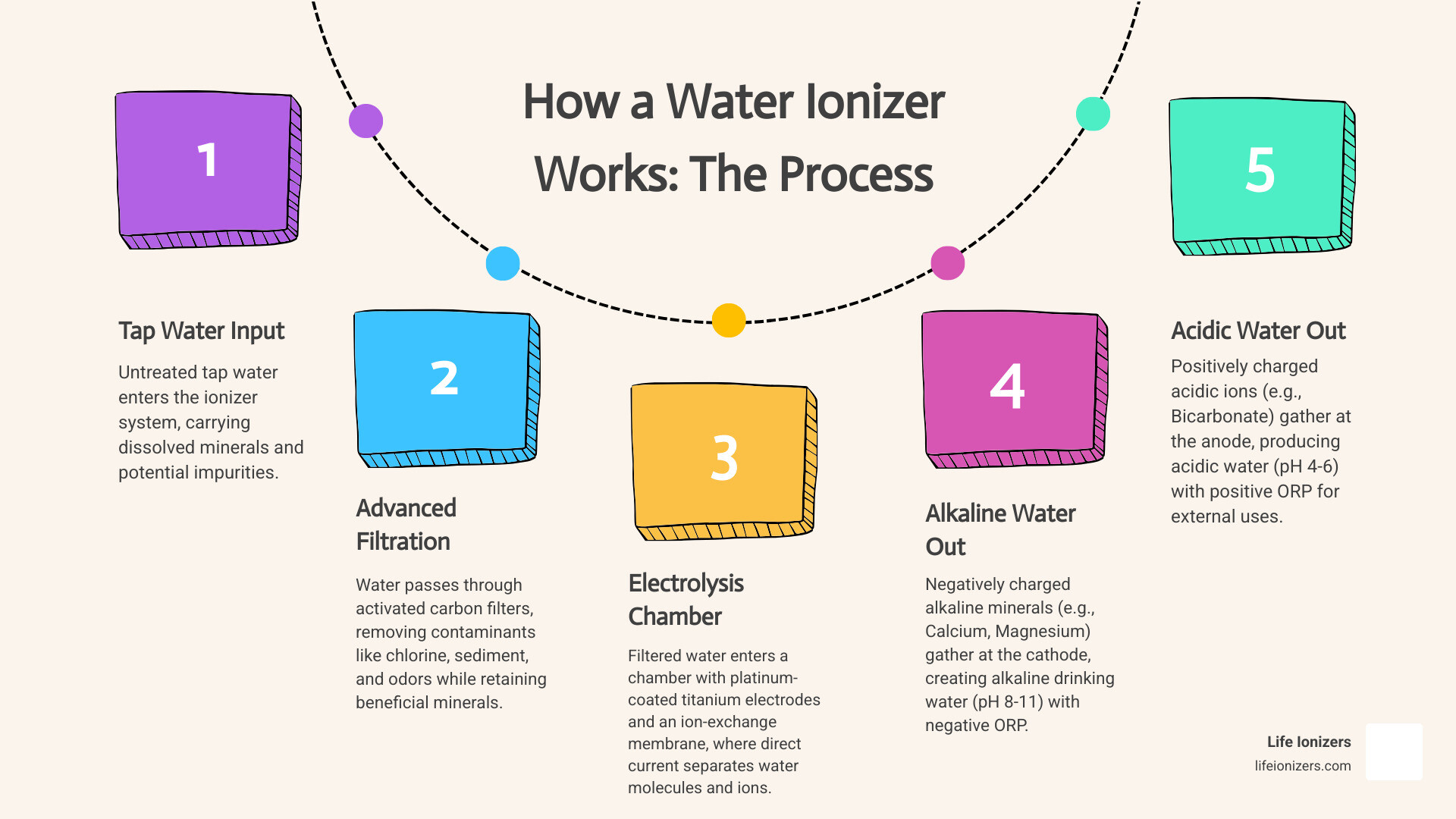
How a water ionizer works is simpler than you might think. It uses a two-step process that first filters tap water, then uses an electrical current (electrolysis) to separate it into two streams: alkaline water for drinking and acidic water for cleaning.
Quick Answer: The 3-Step Process
- Filtration - Water passes through activated carbon filters to remove contaminants like chlorine and sediment while retaining beneficial minerals.
- Electrolysis - The filtered water enters a chamber with platinum-coated titanium electrodes, where electricity separates water into alkaline and acidic components.
- Separation - An ion-permeable membrane divides the water into two streams: alkaline water (pH 8-11) for drinking and acidic water (pH 4-6) for external uses.
Understanding this process can help you make an informed decision about your family's hydration, especially if you're looking for an alternative to costly and wasteful bottled water.
Through electrolysis, these devices separate the naturally occurring minerals in your tap water based on their electrical charge. Alkaline minerals like calcium and magnesium are drawn to the negative electrode, while acidic ions like bicarbonate move to the positive electrode.
I'm Thai Cabados, and for over two decades, I've specialized in water filtration technology, including introducing advanced alkaline hydrogen water systems to the United States. My work focuses on explaining precisely how a water ionizer works, from basic electrolysis to the latest in hydrogen-rich water technology.
What is a Water Ionizer? The Two-Step Change
A water ionizer is a sophisticated device that transforms your tap water. Unlike a simple filter that only removes contaminants, an ionizer changes the water's chemical properties through a two-step process: advanced filtration followed by ionization.
The technology has a long history. Japan's Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare approved these devices as "medical substance generators" in 1965. The technology then spread through East Asia, where devices in Korea require Korean FDA certification. Today, they offer a unique approach to hydration in American homes, backed by decades of use overseas.
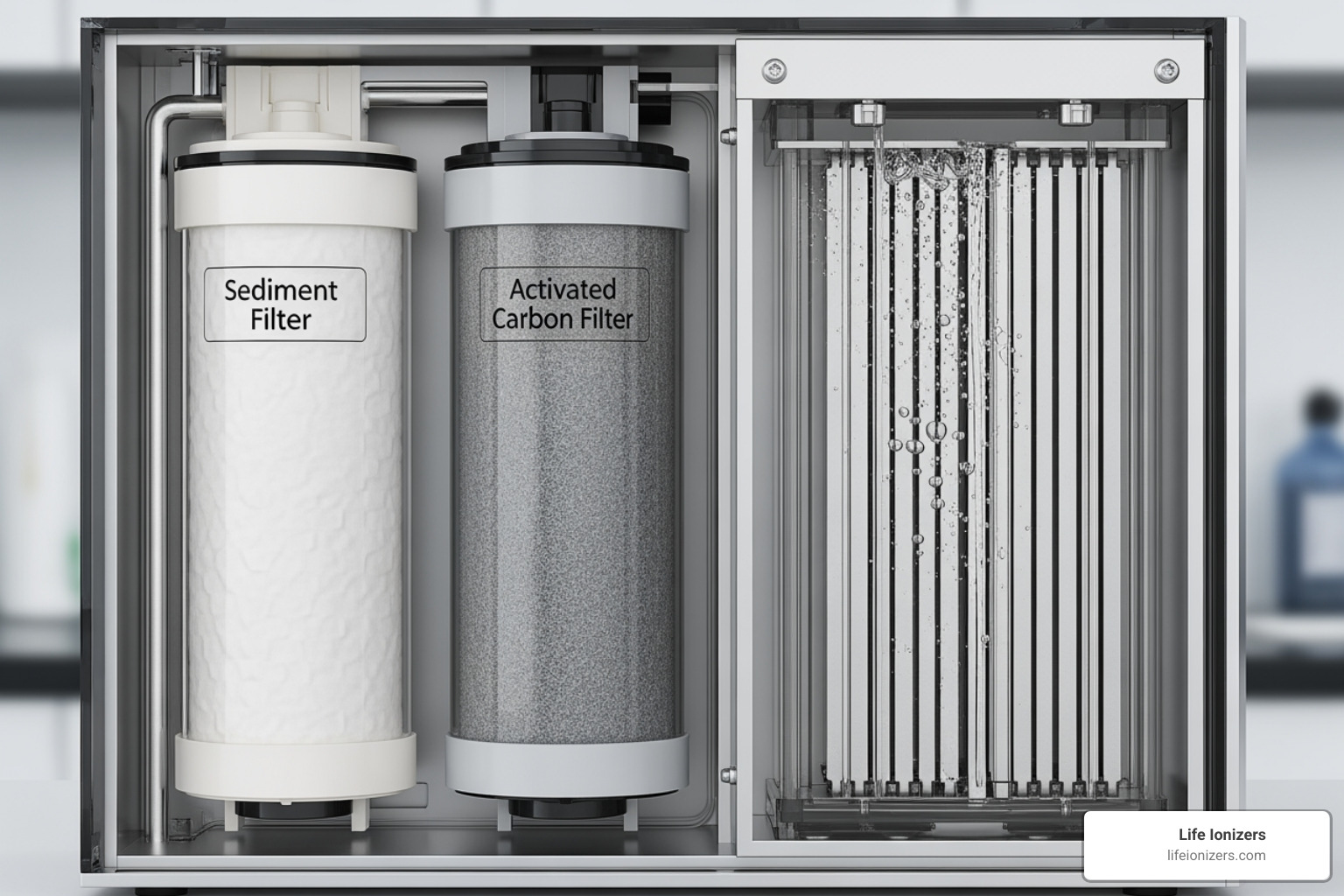

Step 1: Advanced Filtration
Before ionization can occur, water must be clean. The first step in how a water ionizer works is pre-filtration. Your tap water passes through activated carbon filters that remove unwanted substances like chlorine, sediment, odors, and bacteria.
Crucially, these filters are designed to retain beneficial minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium. Unlike reverse osmosis or distillation, which strip everything out, this process keeps the minerals that are essential for the next step: ionization.
Step 2: The Ionization Chamber
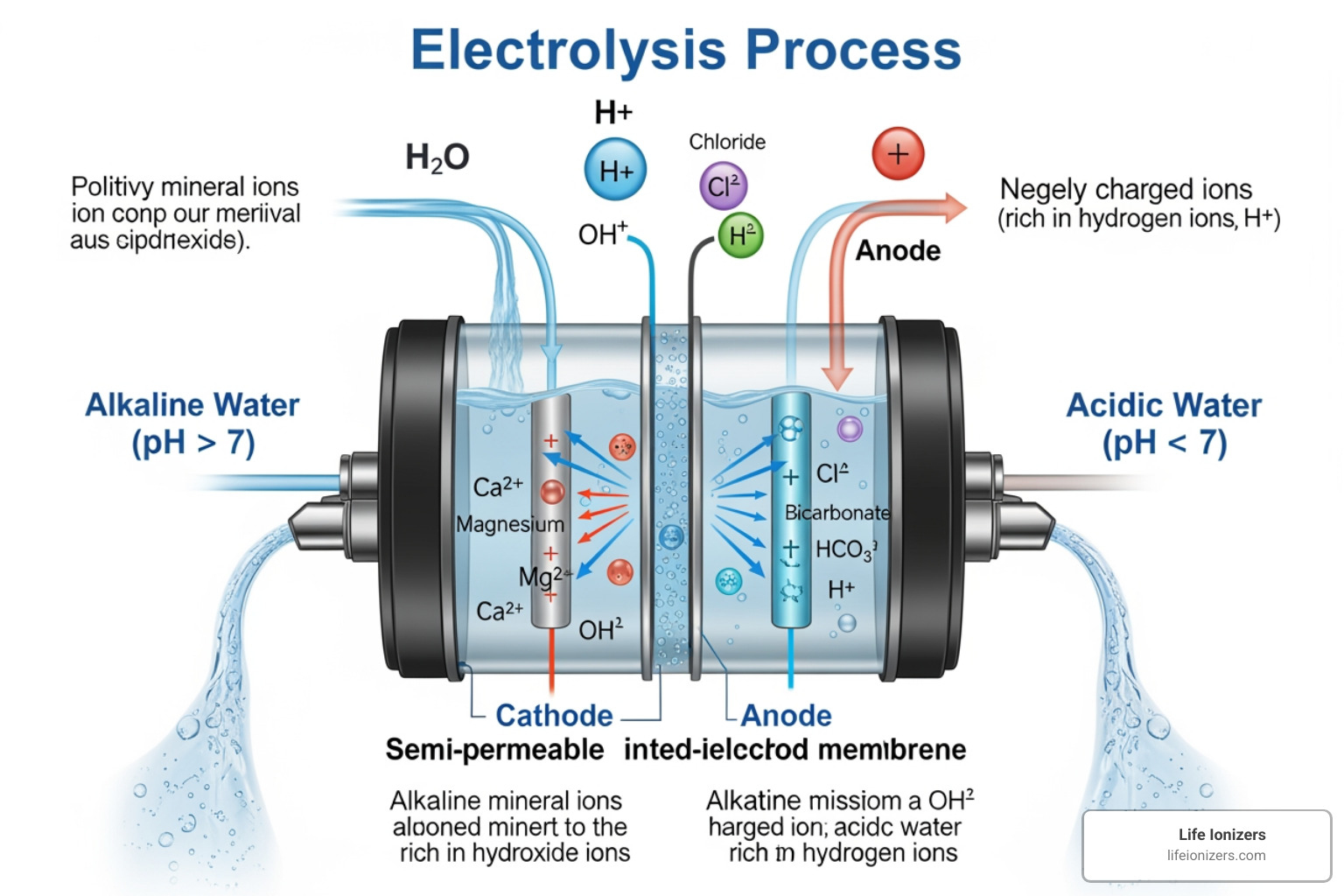
Once filtered, the mineral-rich water flows into the electrolysis chamber—the heart of the machine. Here, the water passes over specialized electrodes separated by an ion-exchange membrane. When direct current (DC) electricity is applied, electrolysis begins, separating mineral ions based on their charge.
The ion-exchange membrane acts as a selective barrier, allowing charged ions to move toward the correct electrode while keeping the two new water streams separate. Positively charged ions (cations) are drawn to the negative electrode, and negatively charged ions (anions) move to the positive electrode. This separation consistently produces two distinct types of water: alkaline water for drinking and acidic water for cleaning.
The Science of Separation: How a Water Ionizer Works via Electrolysis
The core process is electrodialysis, a specialized form of electrolysis that explains how a water ionizer works. Inside the ionization chamber, an electrical current directs the mineral ions in your water. Positively charged minerals (cations) move toward one electrode, while negatively charged ions (anions) flow to the other.
Your mineral-rich water flows over charged plates separated by an ion-permeable membrane. This membrane allows charged mineral ions to pass through but keeps neutral water molecules in place. Positively charged alkaline minerals like calcium and magnesium are pulled toward the negatively charged plates. At the same time, negatively charged acidic ions, such as bicarbonate, move toward the positively charged plates. This separation transforms filtered water into two distinct types.
The Role of Electrodes and the Ion-Exchange Membrane
Our advanced ionizers use platinum-coated titanium electrodes. Titanium provides strength, while the platinum coating is inert, meaning it won't react with or release substances into your water. This ensures purity and durability.
The ion-exchange membrane works alongside the electrodes, acting as a barrier to prevent the newly formed alkaline and acidic waters from mixing. Our proprietary XL Matrix GRID Technology optimizes this process, enhancing surface area and electrical conductivity to produce superior hydrogen-rich, alkaline water more efficiently.
How a Water Ionizer Works: The Chemical Reaction Explained
When electricity flows through the water, the water molecules themselves are affected.
At the negative electrode (cathode), positively charged hydrogen ions (H+) gain electrons and become molecular hydrogen (H2)—the powerful antioxidant in our Live Hydrogen Water™. As H+ ions are converted, hydroxide ions (OH-) increase, raising the pH and making the water alkaline.
At the positive electrode (anode), the opposite occurs. Negatively charged hydroxide ions (OH-) release electrons, forming more H+ ions. This concentration of H+ ions lowers the pH, creating acidic water.
In short: Alkaline water forms at the cathode, where molecular hydrogen (H2) is created and OH- ions increase. Acidic water forms at the anode, where H+ ions accumulate. This precise control over the chemical reactions creates water with specific pH levels and beneficial properties, as explored in studies on the physico-chemical, biological and therapeutic characteristics of electrolyzed reduced alkaline water.
The Two Streams: Understanding Alkaline and Acidic Water
One of the most remarkable features of a water ionizer is its ability to produce two entirely different types of water from a single source: alkaline ionized water and acidic water. We often refer to these as "functional waters" because each stream offers unique properties and a host of practical applications around your home. To understand these differences, we look at two key measurements: pH and Oxidation-Reduction Potential (ORP).
The pH scale, ranging from 0 to 14, tells us how acidic or alkaline water is, with 7 being neutral. ORP, on the other hand, measures the water's ability to act as an antioxidant or an oxidant. A negative ORP indicates antioxidant potential, while a positive ORP indicates oxidizing potential.
Properties of Alkaline Ionized Water: pH, ORP, and Molecular Hydrogen
The alkaline ionized water produced by our machines is what most people are eager to drink. This water typically boasts a pH range of 8-11, making it distinctly alkaline. More importantly, it carries a significant negative ORP, often ranging from -250 to -550mV. This negative ORP signifies its antioxidant potential, meaning it has an excess of electrons available to neutralize harmful free radicals in the body.
This antioxidant power is largely attributed to the presence of molecular hydrogen (H2), which is generated during the electrolysis process. Our XL Matrix GRID Technology is specifically designed to maximize the production of this beneficial molecular hydrogen, providing you with "Live Hydrogen Water™."
Furthermore, this alkaline water is rich in essential mineral hydrates. The electrolysis process concentrates alkaline minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium within this stream. When these mineral ions combine with water molecules after separation, they form mineral hydrates (e.g., calcium hydrate, magnesium hydrate), which contribute to both the pH and the beneficial properties of the water. Research published in Water journal, "Physico-Chemical, Biological and Therapeutic Characteristics of Electrolyzed Reduced Alkaline Water (ERAW)", highlights these unique attributes of electrolyzed reduced alkaline water.
Properties and Uses of Acidic Water
While alkaline water is for drinking, the acidic water stream is incredibly versatile for external uses. This water typically has a lower pH, often in the range of 4-6, and a positive ORP, usually between +350 to +750mV. This positive ORP means it's an excellent oxidizing agent, making it highly effective for cleaning and sterilizing.
Here are just a few of the many uses for the acidic water produced by your ionizer:
- Cleaning & Disinfecting: A chemical-free cleaner for kitchen counters and surfaces.
- Skin Care: Use as a facial toner or astringent to help balance skin pH.
- Hair Rinse: Can make hair softer, shinier, and more manageable.
- Plant Care: Beneficial for acid-loving plants and can help deter fungi.
- Hand Sanitizer: A natural, effective sterilizing agent.
- Mouthwash: Can be used as an antiseptic mouth rinse.
The Health Debate: Claims, Science, and Your Body's pH
Let's address the health claims surrounding alkaline ionized water. As experts who have dedicated decades to understanding how a water ionizer works, we believe in providing the full picture—both the possibilities and the limitations.
Your body is a master of pH regulation through a process called acid-base homeostasis. Your blood remains at a precise 7.4 pH, while your stomach is highly acidic (1.5-3.5 pH) to digest food. When you drink alkaline water, your body quickly adjusts to maintain this balance. The goal isn't to change your body's pH, but to provide water with other beneficial properties.
Common Health Claims Associated with Alkaline Water
Drinking alkaline ionized water has been associated with potential benefits like anti-aging properties, disease prevention, an increase in energy, and better hydration. Many also use it to help neutralize acidic foods in their diet. While many of our customers report feeling better and more energized, it's important to distinguish anecdotal experience from controlled scientific proof.
What Does the Scientific Evidence Say?
The scientific community's position on alkaline water is complex. While smaller studies and anecdotal evidence are plentiful, large-scale evidence for many broad health claims is lacking. For example, a systematic review in BMJ Open found no direct evidence that alkaline water prevents or treats cancer. McGill University's Office for Science and Society has also critiqued sweeping claims in its article "Alkaline Water Nonsense".
However, there is a critical distinction to be made. The research on molecular hydrogen (H2) as an antioxidant and the benefits of water with a negative ORP is a promising and active area of scientific investigation. The unique properties of "Live Hydrogen Water™" are explored in studies like the one on Physico-Chemical, Biological and Therapeutic Characteristics of Electrolyzed Reduced Alkaline Water (ERAW). Our focus is on delivering water rich in molecular hydrogen, which has characteristics that go beyond simple pH.
We encourage you to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice. Water ionizers produce remarkable water, but they are not a cure-all.
Practical Guide: Types, Maintenance, and Choosing the Right Ionizer
Choosing a water ionizer is a commitment to better hydration. Understanding the types, maintenance, and key features will help you make the best choice. The technology has a proven history, with water ionizers earning approval as "medical substance generators" in Japan in 1965. Our Life Ionizers are also recognized by the Korean FDA as medical devices, reflecting the technology's established nature.
Types of Water Ionizers
- Countertop ionizers sit on your counter and connect to your faucet via a diverter valve. Installation is quick (about 10 minutes), and they are portable, making them ideal for renters or those who may move.
- Under-sink ionizers place the main unit under the sink, with a dedicated faucet on the countertop. This provides a clean, integrated look but requires more complex installation.
Your choice depends on your kitchen layout, installation preference, and aesthetic taste.
Essential Maintenance for Longevity and Performance
Proper maintenance is simple and ensures your ionizer performs well for years.
- Filter Replacement: Internal filters should be replaced every 6-12 months, depending on usage and local water quality.
- Automatic Cleaning: Most modern ionizers have automatic cleaning cycles to prevent mineral buildup on the electrodes. Run these cycles weekly.
- Manual Cleaning: A periodic manual descaling may be needed, especially in hard water areas. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for this straightforward process.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Water Ionizer
Cut through the marketing noise by focusing on what truly matters.
- Mineral Retention: Ionization requires minerals. Unlike reverse osmosis systems that strip water of everything, our ionizers retain beneficial minerals like calcium and magnesium, which are essential for electrolysis.
- pH and ORP Range: Look for a machine that offers a wide, adjustable pH range and a consistently strong negative ORP. The negative ORP is your indicator of antioxidant potential and molecular hydrogen production.
- Features and Technology: Convenience features like touch screens are nice, but the internal technology is what counts. Our XL Matrix GRID Technology, for example, is engineered for superior ion separation and maximum hydrogen output.
- Cost: While there is an initial investment, an ionizer can be more cost-effective over time than continuously buying bottled alkaline water.
- Environmental Impact: Using an ionizer significantly reduces plastic waste from single-use water bottles.
- Certifications: Reputable certifications, such as medical device recognition in countries like Japan and Korea, provide peace of mind about the device's safety and effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions about Water Ionizers
We've covered how a water ionizer works, but you may still have questions. Here are answers to the most common ones.
Is ionized water the same as "alkaline water" from a bottle?
No, they are very different. Bottled alkaline water typically gets its high pH from added minerals or salts, like baking soda. It usually has a positive or neutral ORP, meaning it lacks antioxidant potential.
In contrast, ionized water is created through electrolysis. This process not only raises the pH but also fundamentally changes the water's properties, creating a strong negative ORP (e.g., -250 to -550mV) and generating antioxidant molecular hydrogen (H2). This active, fresh "Live Hydrogen Water™" has properties that cannot be bottled and stored on a shelf for months.
Does a water ionizer purify water?
Yes, purification is the crucial first step. Our ionizers contain advanced activated carbon filters that remove common contaminants like chlorine, sediment, and odors. However, a water ionizer is not the same as a reverse osmosis system. It is specifically designed to retain beneficial minerals like calcium and magnesium because they are essential for the electrolysis process to work. For most municipal water, the built-in filtration is sufficient. If your source water has unique challenges like heavy metals, additional pre-filtration may be recommended.
Can I use well water with a water ionizer?
Yes, but with an important preliminary step. Well water is often rich in minerals, which is excellent for ionization. However, it can also contain iron, sulfur, bacteria, or excessive hardness that can interfere with the ionizer's performance.
Before using well water, we strongly recommend a comprehensive water test. Based on the results, you may need a pre-treatment system, such as a sediment filter, iron filter, or UV sterilizer. This ensures your ionizer receives balanced water, allowing it to function optimally and produce the highest quality ionized water.
Conclusion: Changing Your Hydration
So there you have it—the complete story of how a water ionizer works, from the moment tap water enters your machine to the creation of two entirely different streams of functional water. It's a beautiful marriage of advanced filtration and precise electrolysis, changing the water you drink and use every day.
Throughout this article, we've walked through the two-step process: first, the advanced filtration that strips away chlorine, sediment, and contaminants while carefully preserving the beneficial minerals your body needs. Then comes the electrolysis chamber, where those minerals are separated by electrical charge, creating alkaline ionized water rich in molecular hydrogen and antioxidant potential on one side, and versatile acidic water for cleaning and personal care on the other.
The technology isn't magic—it's science. But the results can feel pretty magical when you're drinking water with a negative ORP and beneficial molecular hydrogen, or using chemical-free acidic water to clean your kitchen counters and refresh your skin.
At Life Ionizers, we've dedicated ourselves to perfecting this technology. Our XL Matrix GRID Technology isn't just a fancy name—it's our commitment to producing the highest quality "Live Hydrogen Water™" possible, with superior hydrogen content and antioxidant properties. We believe everyone deserves access to water that supports their health and vitality, not just hydration that's "good enough."
Whether you're in Vista, CA, or anywhere across the United States, making the switch to ionized water means taking control of your hydration quality. It means reducing plastic waste from bottled water while gaining access to both alkaline water for drinking and acidic water for countless household uses. It's an investment in your wellness that pays dividends every single day.
We know choosing a water ionizer is a significant decision. That's why we encourage you to explore all the information available and ask questions. Ready to learn more about what these remarkable machines can do for your daily life? Find What Does a Water Ionizer Do? and see how our ionizers can transform not just your water, but your entire approach to health and wellness.
Your journey to better hydration starts with understanding. And now that you know exactly how a water ionizer works, you're ready to make an informed choice for yourself and your family.

